Ethereum And Ether Exploring Their Impact And Future
With ethereum and ether at the forefront, the decentralized revolution is reshaping how we interact with technology and finance. Picture a world where applications run without intermediaries and digital assets hold real value—this is the promise of Ethereum and its native cryptocurrency, Ether.
Ethereum stands out as a groundbreaking decentralized platform that enables developers to build a plethora of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Ether, as the lifeblood of this ecosystem, fuels transactions and incentivizes network participants, making Ethereum a cornerstone of the blockchain landscape.
Introduction to Ethereum and Ether
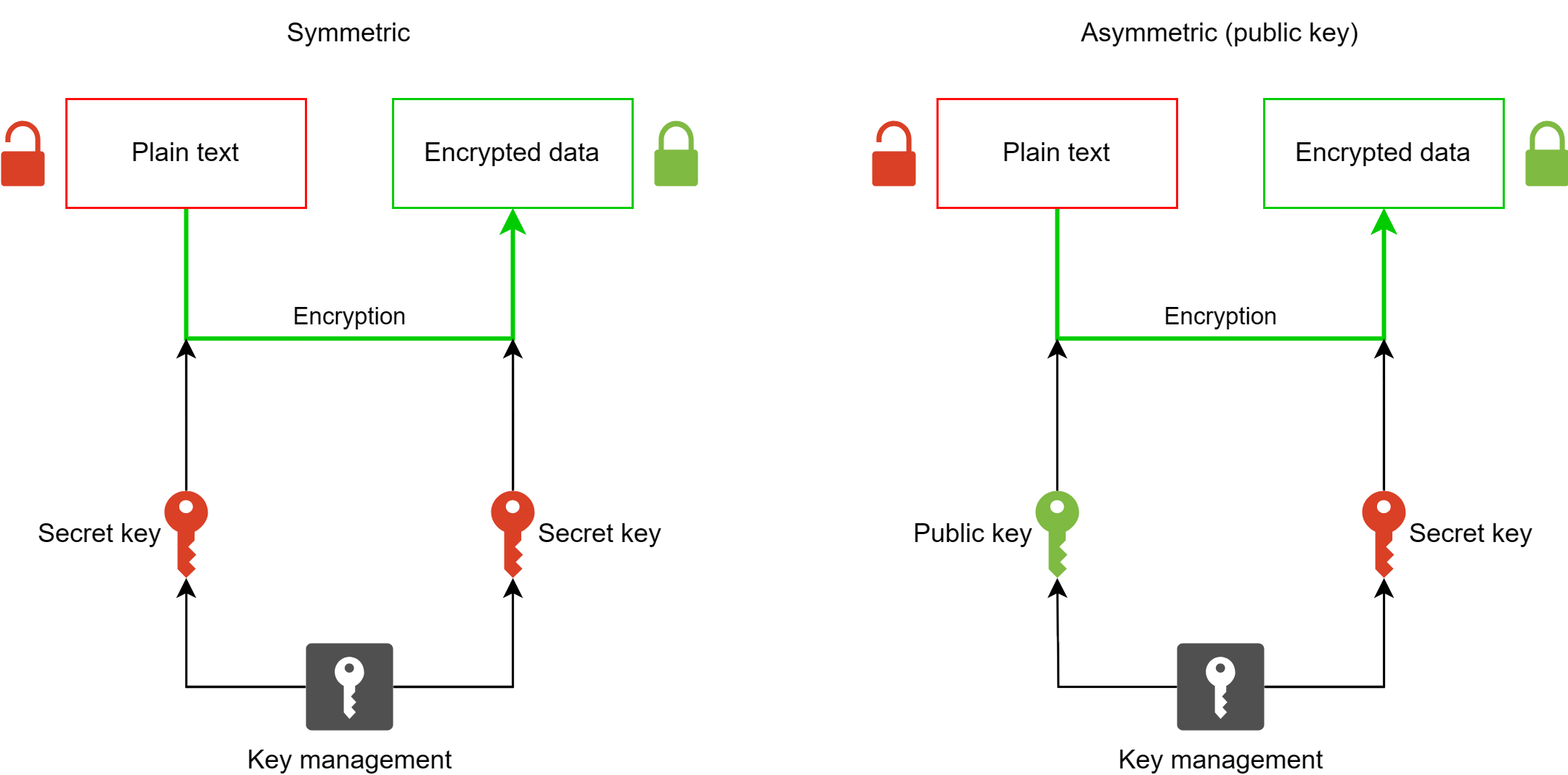
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that enables developers to create and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Unlike traditional centralized systems, Ethereum operates on a blockchain, allowing for trustless interactions among users. Ether, often abbreviated as ETH, serves as the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, facilitating transactions and incentivizing network participants.The significance of Ethereum in the blockchain ecosystem cannot be overstated.
It has introduced a robust framework for building decentralized applications, influencing various sectors from finance to gaming, and has paved the way for innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Technical Overview
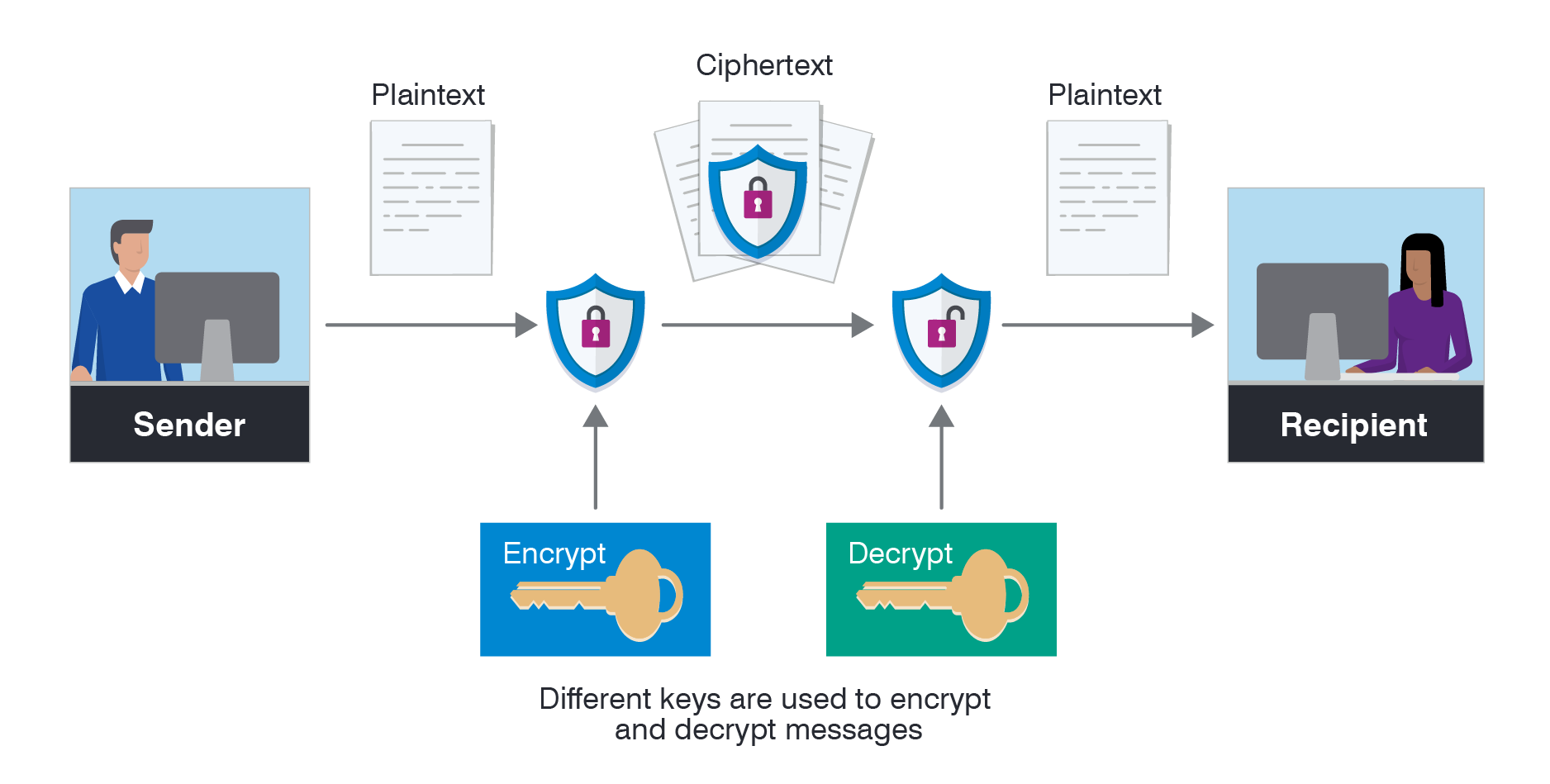
Ethereum's underlying technology is built on the concept of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. This allows for automated and secure transactions without the need for intermediaries. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily serves as a digital currency, Ethereum's versatility extends its functionality to a wide range of applications.Transactions on the Ethereum network are validated through a consensus mechanism known as Proof of Stake (PoS), which is part of the ongoing transition to Ethereum 2.0.
This involves validators who stake their Ether to secure the network rather than miners competing to solve complex puzzles, as seen in Bitcoin.
Use Cases of Ethereum
Ethereum's capabilities have led to a plethora of real-world applications. Its use cases include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms like Uniswap and Aave allow users to trade and lend cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Creators can mint unique digital assets, such as art and collectibles, on platforms like OpenSea.
- Supply Chain Management: Ethereum enables companies to track products in real-time, enhancing transparency and efficiency.
Notable projects utilizing Ethereum include Chainlink, which connects smart contracts with real-world data, and MakerDAO, which provides decentralized lending solutions.
The Ethereum Ecosystem

The Ethereum ecosystem is comprised of various components that contribute to its functionality:
- Wallets: Users can store their Ether and interact with dApps through wallets like MetaMask and Trust Wallet.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): Applications built on Ethereum that provide services ranging from gaming to finance.
- Miners and Validators: These participants maintain network security and validate transactions, earning rewards in Ether.
Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) play a key role in the development of the network, allowing community members to suggest and discuss upgrades or changes to the protocol.
Comparison with Other Blockchain Platforms

While Ethereum is a leader in the blockchain space, it faces competition from platforms like Binance Smart Chain and Cardano. Each of these platforms has its own unique features and trade-offs:
- Ethereum: Offers a robust ecosystem with high adoption but suffers from scalability issues and high gas fees.
- Binance Smart Chain: Provides faster transactions and lower fees, appealing to DeFi projects but may lack decentralization.
- Cardano: Focuses on a research-driven approach to blockchain development and offers scalability solutions, though with a smaller dApp ecosystem.
Choosing Ethereum over other platforms may be preferred for projects requiring a well-established network and a massive user base.
Future of Ethereum and Ether
The transition to Ethereum 2.0 marks a significant advancement for the network, aiming to improve scalability, security, and sustainability. This upgrade will likely lead to increased transaction throughput and reduced energy consumption.Market trends suggest that Ether's value may see substantial growth as adoption increases and more use cases emerge. The integration of scalability solutions, such as sharding, is expected to enhance user experience and support a larger volume of transactions.
Investing in Ether

For those considering investing in Ether, strategies should focus on risk management and market research. It's crucial to diversify investments and stay informed about market trends and technological advancements.Investing in cryptocurrencies carries inherent risks, including market volatility and regulatory changes. Monitoring Ether's market performance involves using tools and resources such as price tracking websites and market analysis platforms.
Community and Governance
The Ethereum community plays a vital role in shaping the network's future. Decision-making processes are often community-driven, with input from developers, users, and stakeholders.Governance within the Ethereum network is facilitated through EIPs and community discussions, ensuring that proposed changes reflect the collective interests of the ecosystem. Initiatives led by community members, such as educational programs and hackathons, have a significant positive impact on the network's growth and adoption.
Epilogue
In summary, Ethereum and Ether represent a significant evolution in the blockchain space, offering innovative solutions and a vibrant ecosystem for developers and users alike. As we navigate the future, the transition to Ethereum 2.0 and the ongoing community initiatives will undoubtedly shape the trajectory of this platform, making it an exciting area to watch.
FAQ Guide
What is the main purpose of Ethereum?
Ethereum acts as a decentralized platform for building applications that run on blockchain technology, enabling smart contracts and various decentralized services.
How does Ether differ from Ethereum?
Ether is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, used for transactions and as a means to compensate participants for validating transactions.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, allowing for automated transactions and processes on the Ethereum network.
How is Ethereum different from Bitcoin?
While Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency, Ethereum is a platform that supports a variety of applications, with its cryptocurrency, Ether, used to power these applications.
What are the risks of investing in Ether?
Investing in Ether carries risks such as market volatility, regulatory changes, and potential technological issues, which can impact its value and usability.