Ethereum Encryption Algorithm And Its Significance
As the ethereum encryption algorithm takes center stage, we delve into its pivotal role in bolstering security and privacy in the blockchain landscape. This algorithm isn’t just a technical component; it serves as the backbone of the Ethereum network, ensuring that data remains secure and transactions are confidential. In a world increasingly reliant on digital assets, understanding the nuances of Ethereum’s encryption is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of blockchain technology.
The significance of encryption algorithms in blockchain cannot be overstated. They provide essential cryptographic security, facilitating trustless transactions and safeguarding user data. Ethereum’s unique approach to encryption sets it apart from other cryptocurrencies, making it indispensable for smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Introduction to Ethereum Encryption Algorithm
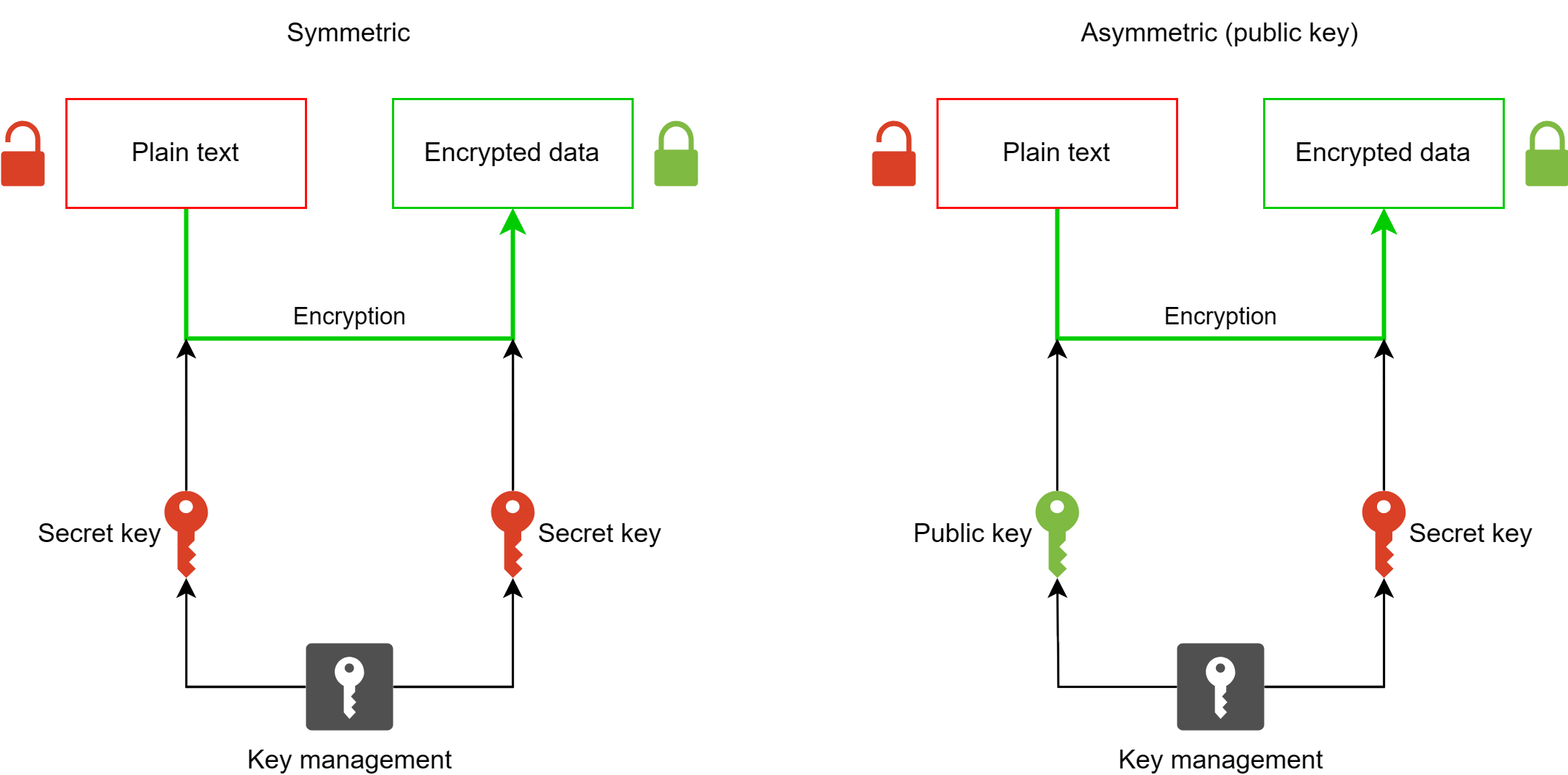
Encryption plays a pivotal role in securing transactions and protecting user data within the Ethereum network. In the context of Ethereum, encryption ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and that transactions are immutable and verifiable. The importance of encryption algorithms in blockchain technology cannot be overstated, as they are fundamental in maintaining trust and security in decentralized systems.Ethereum’s encryption mechanisms distinguish it from other cryptocurrencies through its use of advanced algorithms and innovative features.
Notably, Ethereum employs a combination of hashing and asymmetric encryption techniques, which facilitate secure communication and data integrity across its platform. This not only enhances security but also fosters a conducive environment for decentralized applications to thrive.
Technical Framework of Ethereum Encryption Algorithms
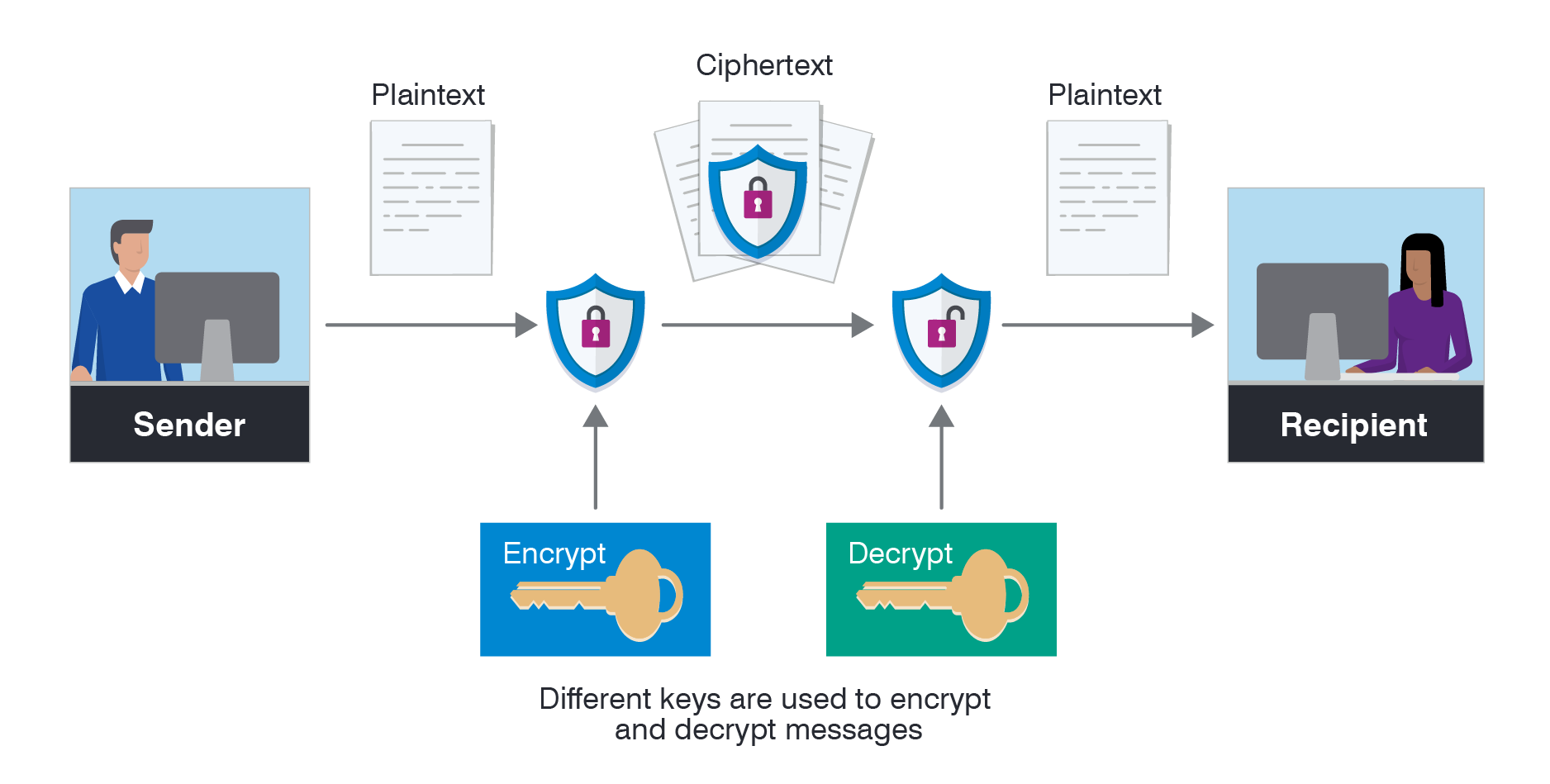
At the core of Ethereum’s encryption framework are several essential algorithms, including the Keccak-256 hashing algorithm. This algorithm is integral to the Ethereum blockchain, as it secures block transactions and creates a unique fingerprint for each block. Additionally, Ethereum utilizes the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) for its public key cryptography, ensuring that transactions are signed securely.The process of data encryption within the Ethereum network involves multiple steps.
Initially, when a transaction is initiated, it is hashed using Keccak-256, producing a unique identifier. This identifier is then encrypted with the sender’s private key, allowing only the intended recipient, who possesses the corresponding public key, to decrypt the information.Public and private keys play a crucial role in Ethereum’s encryption mechanism. The private key is known only to the owner and is vital for signing transactions, while the public key is distributed widely, allowing others to verify the authenticity of the transactions associated with that key.
This asymmetric nature of key management enhances security by ensuring that even if the public key is compromised, the private key remains secure.
Comparison with Other Blockchain Encryption Methods
When comparing Ethereum’s encryption algorithms with those of Bitcoin, there are notable differences in approach and functionality. While Bitcoin primarily uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm for transaction verification, Ethereum’s use of Keccak-256 provides enhanced security features and efficiency.The advantages of Ethereum’s encryption approach include:
- Increased transaction speed and efficiency due to the optimized hashing mechanism.
- Support for complex smart contracts, enabling more advanced functionality compared to Bitcoin.
However, there are also disadvantages, such as:
- Potentially larger attack surfaces due to the added complexity of smart contracts.
- Increased computational requirements, which can lead to higher transaction fees during network congestion.
This evolution of encryption algorithms in blockchain technologies reflects the ongoing need for enhanced security measures as the ecosystem matures.
Applications of Ethereum Encryption in Smart Contracts
Encryption underpins the security of smart contracts on the Ethereum platform, ensuring that contractual agreements are executed as intended without the risk of tampering. For instance, when a smart contract is deployed, its code is hashed and stored on the blockchain, and any interactions with it are securely encrypted, safeguarding sensitive data and making it resistant to unauthorized access.Examples of how Ethereum encryption enhances transaction privacy include:
- Utilization of zero-knowledge proofs, which allow one party to prove possession of certain information without revealing the information itself.
- Implementation of privacy-focused layers, such as zk-SNARKs, which further obfuscate transaction details while maintaining validation.
The implications of encryption for decentralized applications (dApps) are significant; they ensure user interactions and data remain private, thereby fostering trust among users and encouraging broader adoption of the Ethereum platform.
Security Challenges and Vulnerabilities
Despite the robust encryption algorithms employed by Ethereum, potential security threats still persist. Common threats include malicious attacks targeting smart contracts, which can exploit vulnerabilities in the code, leading to unauthorized fund access or contract manipulation.Historical instances of vulnerabilities have impacted the Ethereum network, such as the infamous DAO hack in 2016, where attackers exploited a flaw in the smart contract code, resulting in the loss of millions of dollars.
This incident underscored the need for rigorous auditing and testing of smart contracts before deployment.To enhance the security of Ethereum encryption, several measures have been implemented, including the introduction of development best practices, automated testing tools, and community-led audits. The Ethereum Foundation continues to advocate for security awareness among developers to mitigate risks associated with smart contracts and encryption algorithms.
Future Developments and Innovations
Ongoing research aims to improve Ethereum’s encryption algorithms, focusing on scalability, efficiency, and enhanced security features. Innovations like sharding and layer-2 solutions are being explored to alleviate congestion on the main network and improve transaction throughput.Potential future trends in encryption for blockchain technologies may include:
- Adoption of post-quantum cryptography to prepare for the advent of quantum computing, which poses a threat to current encryption methods.
- Integration of decentralized identity solutions, allowing users to control their data more effectively while maintaining privacy.
Advancements in encryption will significantly influence Ethereum’s scalability and performance, enabling the network to handle a higher volume of transactions without compromising security, ultimately fostering greater adoption and utility for decentralized applications.
Ending Remarks

In summary, the ethereum encryption algorithm is more than just a technical framework; it is a vital element that ensures the integrity and security of transactions within the Ethereum ecosystem. As we look to the future, ongoing advancements in encryption technology promise to enhance both scalability and performance, further solidifying Ethereum’s position as a leader in blockchain innovation. Understanding these elements will empower users and developers alike to engage with this transformative technology more effectively.
Expert Answers
What makes Ethereum’s encryption unique?
Ethereum’s encryption combines public and private key cryptography, enabling secure transactions and smart contract execution.
How does Ethereum ensure transaction privacy?
Ethereum utilizes advanced encryption techniques to obscure transaction details while maintaining network transparency.
Are there any known vulnerabilities in Ethereum’s encryption?
Yes, there have been historical vulnerabilities, but ongoing research aims to enhance security measures continually.
How do encryption algorithms impact Ethereum’s scalability?
Improvements in encryption algorithms can enhance processing speeds, thus positively influencing Ethereum’s scalability.
What is the future of encryption in blockchain technology?
Future trends indicate a focus on developing more efficient and robust encryption methods to address emerging security challenges.